-
GeneralGeneral
-
Obstetrics and Gynecologic Homepage


Welcome to our Obstetrics and Gynecology: Resource Library for Medical Students. This digital repository is dedicated to equipping you with essential knowledge and skills in obstetrics and gynecology. Dive into various resources spanning critical topics — from maternal health and reproductive science to specific clinical practices in the specialty.
Our library has been meticulously curated, grounding itself in the “APGO's Medical Student Education Objectives.” Like all NextGenU.org materials, this library was developed as a joint effort of expert instructional designers and subject matter experts. The subject matter expert involved in reviewing these materials is Vaneza Valentina L. Penolio, MD, FPOGS, FPSRM, FPSGE, FPSUOG, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of Bicol Regional Hospital and Medical Center and Vasant Basdeo, MD. Primary Care Physician. Our instructional designers participating in the development of this library are Alixandria Ali, BSc; Pablo Baldiviezo, MD, MSc; Carolina Bustillos, MD, DiplEd; Daniel Luna, MD, DiplEd; and Shivani Boodram, PhD, BSc.
The library is enriched with resources from globally recognized institutions: the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO), the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO), the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), and World Health Organization (WHO), to name a few.
For publications on the efficacy of NextGenU.org’s courses, see our publication page.
This library is divided into five modules:
- Module 1: Introduction to Patient Attention
- Module 2: Obstetrics
- Module 3: Gynecology
- Module 4: Reproductive Endocrinology, Infertility, and Other Related Topics
- Module 5: Neoplasia
- Module 6: Human Sexuality
- Module 7: Violence Against Women
- Module 8: Osteopathy Women’s Health Care
Beyond textual content, the library harnesses multimedia elements like videos. These are case scenarios presented in discussion forum formats, leveraging the power of collective insights, fostering critical thinking, and promoting collaborative learning.
- Readings: Offer foundational knowledge with comprehensive details for a deep understanding. They support self-paced learning, allowing you to achieve mastery over concepts.
- Videos: Complement readings by visually representing complex procedures and concepts. They enhance the grasp of practical aspects, like surgeries and patient interactions, which are crucial in ObGyn.
- Case Scenarios in Discussion Forums: Bridge theoretical knowledge with real-world application. These interactive forums promote peer-to-peer learning, fostering clinical reasoning and communication skills while simulating real-life clinical situations.
Engaging with this library:
You may browse these resources for free; there are no requirements. We hope that you will find this a rewarding learning experience. Subscribe to our newsletter to be notified of future updates, including interactive case studies and quizzes to complement this library.
Professional Ethics:
It is imperative to acknowledge and act within the perimeter of one's skills. Always extend care within the boundaries of your expertise. If a situation arises that exceeds your knowledge or experience, it is not only acceptable but crucial to seek guidance from seasoned health workers. This manual is an invaluable tool, yet it cannot replace the nuanced learning derived from hands-on training with a seasoned instructor. Embrace every opportunity to augment your skills and knowledge.
In our curriculum, the topic of abortion is addressed with the utmost seriousness and respect. We prioritize reducing maternal mortality due to unsafe abortions by emphasizing the need for rigorous training and professional, safe abortion practices. We stand by the principle that every medical professional should be equipped with comprehensive knowledge to safeguard the well-being of every patient.
-
Module 1: Introduction to Patient Attention
This module aims to develop your competence in the medical interview and physical examination of women while emphasizing the importance of ethical, social, and diverse perspectives in providing culturally competent health care. You will learn to conduct comprehensive women's medical interviews covering various domains and assess risks for different health conditions. Additionally, you will gain skills in performing sensitive physical examinations, such as breast and pelvic exams. The module will also cover topics like cervical cancer and STI screening, diagnosis and management planning, emotional dimensions and interpersonal communication, legal and ethical issues, and preventive care and health maintenance. By completing this module, you'll be equipped to provide holistic care, address patient needs, and consider socio-cultural factors in your practice. Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
-
Module 1: Lesson 1: History
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Complete a comprehensive women’s medical interview, including: Gyneco/Obstetric history, Family/genetic history and present illnes in general.
- Assess risk for unintended pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections, cervical dysplasia, breast malignancy, gynecologic malignancies, nutrition/obesity, domestic violence, and eating disorders in the context of population health, including social and environmental factors.
- Recommend screening tests for malignancy, infection, and other conditions, with consideration of population health and value-based care.
- Demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that build trust by addressing relevant factors, including culture, ethnicity, language/literacy, socioeconomic status, spirituality/ religion, age, sexual orientation, and disability.
- Produce well-organized written and oral reports to communicate the results of the ob-gyn and general medical interview
7 URLs - Complete a comprehensive women’s medical interview, including: Gyneco/Obstetric history, Family/genetic history and present illnes in general.
-
Module 1: Lesson 2: Examination
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the Normal female anatomy and the appearance of common pathology of the urogenital tract and of common breast changes and disorders.
- Describe the female reproductive system pelvic organs and their relevance to perform a physical examination.
- Describe the recommendations for screening breast and pelvic examinations in women’s health care maintenance, with consideration of population health and value-based care.
- Demonstrate interpersonal communication skills to establish trust and cooperation between patient and provider and assure patient’s comfort and dignity.
- Perform accurate examinations in a sensitive manner, including the examination breast, abdominal, complete pelvic and the general body.
- Demonstrate the ability to conduct a thorough and comprehensive health assessment of the patient, taking into account their physical, emotional, and psychological status.
- Producewell-organized written and oral reports to communicate findings of the examination.
- Communicate examination findings with the patient using language commensurate with level of health literacy.
10 URLs - Describe the Normal female anatomy and the appearance of common pathology of the urogenital tract and of common breast changes and disorders.
-
Module 1: Lesson 3: Cervical Cancer and Sexually Transmitted Infection Screening
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the indications for cervical cancer and Sexually Transmitted Infection screening, with consideration of population health and value-based care.
- Obtain specimens for cervical cancer screening, including cytology and Human papillomavirus testing.
- Obtain specimens to detect sexually transmitted infections.
- Explain to the patient the purpose of cervical cancer and Sexually Transmitted Infection screening, and the impact on population health, in language commensurate with level of health literacy.
- Describe the role of cervical cancer and Sexually Transmitted Infection screening in improving population health outcomes.
6 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 1: Lesson 4: Diagnosis and Management Plan
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Generate a problem list.
- Formulate a diagnostic impression, including differential diagnosis
Describe clinical reasoning process to arrive at diagnoses, with interpretation of relevant confirming and disconfirming findings. - Appraise cultural, psychosocial, economic, and ethical issues in patient care.
- Describe the role cognitive biases may play in the diagnostic process.
- Develop a management plan, with consideration of value-based care and of social, cultural, and economic factors that may affect access to and utilization of health care:
1. Laboratory and diagnostic studies
2. Treatment options, including medical, surgical, and lifestyle modifications
3. Patient education commensurate with level of health literacy
4. Continuing care plans
2 URLs - Generate a problem list.
-
Module 1: Lesson 5: Emotional Dimensions and Interpersonal Communication
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand the emotional changes, challenges, and needs associated with different stages of a woman's life, especially as they pertain to gynecological health.
- Comprehend the relevance and management of Premenstrual dysphoric disorder, depression, grief, palliative care, and hospice care within the context of gynecology.
- Understand the emotional aspects of sexual development, considering cultural, social, and individual factors.
- Develop an ability to provide holistic care, addressing both physical and emotional needs, especially in contexts like palliative and hospice care.
- Reflect on feedback specifically related to addressing emotional features in gynecology, and implementing changes in practice for improved patient care.
7 URLs -
Module 1: Lesson 6: Legal and Ethical Issues in Obstetrics and Gynecology
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Explain the following legal/ ethical issues in Gynecology and Obstetrics Patients:
1. Informed consent for procedures, tests or treatment
2. Confidentiality
3. Advance directives for healthcare
4. Screening and reporting of suspected child abuse, sexual abuse, and intimate partner violence. - Discuss legal and ethical issues in provision of reproductive health care to minors.
- Discuss the foundational principles of bioethics and their relevance in gynecological scenarios.
- Apply bioethical principles in practical situations to resolve conflicts arising from differing perspectives, including patient autonomy, clinician recommendations, and societal norms.
- Discuss the legal and ethical issues of pain management and opioid addiction in obstetrics and gynecology.
- Describe issues of justice relating to reproductive health care access.
- Describe the social and structural determinants of health that may influence access to health care and medical decision-making.
- Recognize his/her role as a leader and advocate for women.
- Recognize the ethical issues of other specialties and disciplines as they relate to women’s health care.
13 URLs, 1 Forum - Explain the following legal/ ethical issues in Gynecology and Obstetrics Patients:
-
Module 1: Lesson 7: Preventive Care and Health Maintenance
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students will be able to:- Acquire proficiency in executing standard gynecology office procedures safely and effectively.
- Counsel patients regarding the following and suggest appropriate referral if necessary (i.e. social worker, nutritionist, psychologist): Contraception, Violence, Sexually infections, Exercise, Depression, Substance abuse among others.
- Explain prevention guidelines, including screening procedures, with an understanding of value-based care for diseases of the organs and systems involved in gynecology and obstetrics process
- Identify risk factors in a patient’s personal and family history, including socio-economic status and status as member of racial, ethnic or gender minority, for diseases of the the organs and systems involved in gynecology and obstetrics process.
- Advise patients on a broad range of preventive and proactive measures to maintain a state of wellness, including regular medical check-ups, balanced diet, exercise, and mental well-being.
- Identify barriers to accessing preventive health care services:
1. Personal (social, economic, insurance)
2. Provider (implicit bias, stereotyping)
3. Community/ Local (transportation, facility access, hours of operation)
4. Regional
5. National
4 URLs -
Module 2: Obstetrics
This comprehensive module covers a wide range of topics related to maternal and fetal health. You will learn about the physiological and anatomical changes of pregnancy, fetal and placental physiology, diagnostic studies for assessing fetal well-being, and preconception screening based on risk factors. The module also addresses genetic risks, substance abuse, intimate partner violence, nutrition, mental health, environmental hazards, and folic acid intake. Additionally, you will explore ethical issues in prenatal genetic screening, gestational age determination, normal pregnancy diagnostic studies, newborn care, postpartum complications, breastfeeding benefits, medication safety during breastfeeding, pregnancy termination, and common medical and surgical conditions in pregnancy. By completing this module, you will be well-equipped to provide comprehensive and patient-centered care during the reproductive journey. Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
-
Module 2: Lesson 1: Maternal-Fetal Physiology
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Discuss the maternal physiologic and anatomic changes associated with pregnancy.
- Describe fetal physiology.
- Describe placental physiology.
- Interpret common diagnostic studies of fetal well-being during pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care.
4 URLs - Discuss the maternal physiologic and anatomic changes associated with pregnancy.
-
Module 2: Lesson 2: Preconception Care
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe preconception screening for common medical conditions based on risk factors, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe recommended preconception immunizations.
- Assess paternal and maternal contributions to genetic risks to pregnancy and child well-being, with consideration of value-based care, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Describe genetic screening options in pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Recognize a patient’s risk of substance abuse and intimate partner violence, and explain how this would be addressed with a patient as part of an interprofessional team.
- Appraise a patient’s nutritional status and make recommendations to the patient on nutrition and exercise, with consideration of value-based care, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Appraise a patient’s oral health, with consideration of value-based care, and make recommendations for dental care.
- Appraise a patient’s mental health and make recommendations for mental/ behavioral health referrals, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Assess a patient’s environmental hazards in pregnancy, with consideration of social and economic determinants of risk exposure.
- Explain recommendations for folic acid intake for prevention of birth defects.
- Identify ethical issues associated with prenatal genetic screening and diagnostic tests, with consideration of value-based care, as part of an interprofessional team.
13 URLs - Describe preconception screening for common medical conditions based on risk factors, with consideration of value-based care.
-
Module 2: Lesson 3: Antepartum Care
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Diagnose pregnancy.
- Determine gestational age and use of antenatal card.
- Assess risk factors for pregnancy complications, including screening for intimate partner violence.
- Describe appropriate screening tests and timing for normal pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe appropriate diagnostic studies and timing for normal pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care.
- List the nutritional needs of pregnant women.
- Identify adverse effects of drugs and environmental factors on pregnancy.
- Perform a physical examination on obstetric patient according gestational age.
- Discuss answers to commonly asked questions concerning pregnancy, labor, and delivery.
- Describe approaches to assessing the following:
1. Fetal well-being
2. Fetal growth
3. Amniotic fluid volume
4. Fetal lung maturity - Describe the impact of pregnancy on medical conditions and the impact of medical conditions on pregnancy.
- Describe the effects of pregnancy on women’s social and economic roles.
7 URLs - Diagnose pregnancy.
-
Module 2: Lesson 4: Intrapartum Care
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Differentiate between the signs and symptoms of true labor and false labor.
- Perform initial assessment of a laboring patient, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe the four stages of labor and recognize common abnormalities.
- Explain pain management approaches during labor within a framework of interprofessional teamwork.
- Describe methods of monitoring the mother and fetus, with consideration of patient safety and value-based care.
- Describe the steps of a vaginal delivery.
- List indications for operative delivery, with consideration of patient safety.
- Describe the steps of a Cesarean delivery, with consideration of patient safety and an approach to improve the quality of care for surgical interventions.
- Identify maternal and fetal risks specific to delivery in low-resource settings.
- Describe the role of a multidisciplinary and interprofessional team in providing intrapartum care.
10 URLs - Differentiate between the signs and symptoms of true labor and false labor.
-
Module 2: Lesson 5: Immediate Care of the Newborn
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List techniques for assessing newborn status within a framework of interprofessional teamwork.
- Describe immediate care of the normal newborn, with consideration of value-based care.
- Recognize findings requiring immediate intervention in newborn care.
- Describe the risks and benefits of male infant circumcision, with consideration for patient safety and recognition of cultural and social factors.
1 URL, 1 Forum -
Module 2: Lesson 6: Postpartum Care
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define Puerperium and its stages.
- Describe normal maternal physiological changes of the postpartum period.
- Describe the components of postpartum care, with consideration of value-based care and social, racial and economic disparities in postpartum outcomes.
- Explain the immediate postpartum care for vaginal deliveries, including monitoring of the parturient and fluid administration.
- Diagnose and evaluate potential postpartum complications, identifying common issues such as postpartum hemorrhage (early or late), vulvar/vaginal hematoma, surgical site infections, and more.
- Describe postpartum patient counseling, including risk factors for medical and mental health complications.
- Outline discharge instructions and out-patient follow-up visits, encompassing:
- Perineal/wound care
- Ambulation
- Diet recommendations
- Bladder and bowel function monitoring
- Pain management strategies
- Describe postpartum contraception options, with consideration of value-based care and opportunities for advocacy
7 URLs, 1 Forum - Define Puerperium and its stages.
-
Module 2: Lesson 7: Lactation and Breastfeeding
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the normal physiologic and anatomic changes of the breast during pregnancy and postpartum.
- Diagnose and recommend treatment for common postpartum abnormalities of the breast, with consideration of value-based care.
- List the benefits of breastfeeding, with an understanding of social, economic, ethnic and racial disparities in health outcomes for breastfeeding patients and their infants, and opportunities for advocacy.
- Describe the resources and approach to determining medication safety during breastfeeding with a framework for interprofessional teamwork.
- Describe common challenges in the initiation and maintenance of lactation, recognizing social and structural determinants of health that may affect breastfeeding.
- Promote the advantages of breastfeeding for both mother and baby through education and referral to specialist consultants.
- Solve common challenges faced during the initiation of breastfeeding.
- Identify common complications related to breastfeeding.
- Describe the WHO/UNICEF 10 steps to successful breastfeeding.
8 URLs - List the normal physiologic and anatomic changes of the breast during pregnancy and postpartum.
-
Module 2: Lesson 8: Ectopic Pregnancy
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Identify signs and symptoms of extrauterine pregnancy.
- Develop a differential diagnosis for vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain in the first trimester.
- Perform a physical exam to assess for acute abdomen.
- List risk factors for ectopic pregnancy, with an understanding of ethnic and racial disparities in health outcomes for women who experience ectopic pregnancy and opportunities for advocacy.
- Discuss diagnostic protocols for ectopic pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
- Describe treatment options for patients with ectopic pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
3 URLs, 1 Forum - Identify signs and symptoms of extrauterine pregnancy.
-
Module 2: Lesson 9: Spontaneous Abortion
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Develop a differential diagnosis for first trimester vaginal bleeding.
- Describe the types of spontaneous abortions (missed, complete, incomplete, threatened, inevitable, septic).
- List causes of spontaneous abortion, with consideration of ethnic, racial and cultural disparities in health outcomes.
- List common complications of spontaneous abortion, with consideration of social and structural determinants of health outcomes.
- Discuss treatment options for spontaneous abortion, with consideration for patient safety and value-based care.
- Recognize the psychological impact of spontaneous abortion on patients and their families, and the role of mental/behavioral health services.
4 URLs - Develop a differential diagnosis for first trimester vaginal bleeding.
-
Module 2: Lesson 10: Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand and identify the clinical criteria for Recurrent Pregnancy Loss.
- Recognize the prevalence and key risk factors associated with RPL.
- Recommend behavior modifications to reduce RPL risks.
- Discern indications for and interpret results of genetic, thrombophilia, immunologic, metabolic, and endocrinologic tests.
- Familiarize with medical and surgical treatment for RPL.
- Provide empathetic counseling on RPL's psychosocial impacts and guide on future pregnancies.
2 URLs - Understand and identify the clinical criteria for Recurrent Pregnancy Loss.
-
Module 2: Lesson 11: Pregnancy Termination
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand the ethical obligations of a healthcare provider in the context of pregnancy termination, emphasizing patient safety and rights.
- Differentiate between legal and illegal practices surrounding pregnancy termination in the jurisdiction of practice.
- Understand and adhere to the legal guidelines of pregnancy termination in the jurisdiction of practice, recognizing the ethical responsibilities towards patient safety and rights.
- Provide nondirective counseling to patients surrounding pregnancy, including unintended pregnancy, and discuss how health policy and advocacy, as well as social and environmental factors, impact reproductive rights in health care.
- List surgical and non-surgical methods of pregnancy termination, with consideration of value-based care.
- Identify potential complications and patient safety implications of pregnancy termination.
- Describe the public health impact of the legal status of abortion, and discuss how health policy and advocacy, as well as social and environmental factors, impact access to abortion.
8 URLs - Understand the ethical obligations of a healthcare provider in the context of pregnancy termination, emphasizing patient safety and rights.
-
Module 2: Lesson 12: Medical and Surgical Complications of Pregnancy
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Recognize and describe the following medical and surgical conditions in pregnancy, including their impact on the care and safety of both the gravid patient and the fetus/newborn, the appropriate initial history, physical examination and diagnostic evaluation, and the impact of social and environmental factors on the management of:
- 1. Anemia
- 2. Endocrine disorders, including diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease
- 3. Cardiovascular disease
- 4. Hypertension
- 5. Pulmonary disease, including asthma, Tb, URI
- 6. Renal disease
- 7. Common gastrointestinal diseases, including GERD, gastroenteritis, cholecystitis, cholestasis
- 8. Common neurologic conditions, including epilepsy, migraine, carpal tunnel syndrome, Bell’s palsy, multiple sclerosis
- 9. Autoimmune disorders, including SLE and rheumatoid arthritis
- 10. Alcohol, tobacco, and substance abuse, including opioids
- 11. Surgical abdomen
- 12. Infectious diseases, including
a) Syphilis
b) TORCH (Toxoplasmosis, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes)
c) Group B Streptococcus
d) Hepatitis
e) Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
f) Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and other sexually transmitted infections
g) Parvovirus h) Varicella - 13. Trauma and injury, including intimate partner violence, gun injury and motor vehicle injury
13 URLs - Recognize and describe the following medical and surgical conditions in pregnancy, including their impact on the care and safety of both the gravid patient and the fetus/newborn, the appropriate initial history, physical examination and diagnostic evaluation, and the impact of social and environmental factors on the management of:
-
Module 2: Lesson 13: Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define types of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
- Describe the pathophysiology of preeclampsia.
- Discuss risk factors for preeclampsiaeclampsia, including social and environmental factors.
- Recognize the signs, symptoms, and diagnostic criteria of preeclampsiaeclampsia, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe the management of preeclampsiaeclampsia at term and remote from term, including the role of the multidisciplinary team.
- Discuss maternal and fetal complications and patient safety implications associated with preeclampsia, recognizing disparities in health outcomes related to social factors.
8 URLs, 1 Forum - Define types of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
-
Module 2: Lesson 14: Alloimmunization
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the pathophysiology and diagnosis of alloimmunization.
- Describe the use of immunoglobulin prophylaxis during pregnancy for the prevention of alloimmunization.
- Discuss the multidisciplinary management of a patient with Rh-D sensitization in pregnancy.
2 URLs - Describe the pathophysiology and diagnosis of alloimmunization.
-
Module 2: Lesson 15: Multifetal Gestation
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the risk factors for multifetal gestation.
- Describe the embryology of multifetal gestation.
- Describe maternal and fetal physiologic changes associated with multifetal gestation.
- Describe diagnosis and multidisciplinary management of multifetal gestation (multifetal monitoring and birth planning).
- Describe the potential maternal and fetal complications and safety concerns associated with multifetal gestation.
2 URLs - List the risk factors for multifetal gestation.
-
Module 2: Lesson 16: Fetal Demise
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the symptoms and common causes of fetal demise in each trimester, including genetic, social, environmental, and nutritional factors
- Describe the diagnosis and management of fetal demise, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
- Describe the multidisciplinary team approach to medical and psychosocial management of fetal demise.
- Describe the steps to disclose a diagnosis of fetal demise to a patient.
- Identify factors unique to low resource settings, including social, cultural, and environmental factors that may lead to fetal demise.
1 URL -
Module 2: Lesson 17: Abnormal Labor
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define abnormal labor patterns.
- Describe the possible etiologies of abnormal labor, with an understanding of the role of social and environmental factors on the risk of developing abnormal labor.
- Describe methods of evaluating labor patterns and the role of nursing professionals and midwives in diagnosis of abnormal labor, with consideration of value-based care.
- Discuss fetal and maternal complications of abnormal labor.
- List indications and contraindications for oxytocin administration, with consideration of patient safety.
- Describe risks and benefits of trial of labor after Cesarean delivery.
- Discuss strategies for emergency management of breech presentation, shoulder dystocia, and cord prolapse, including the role of the interprofessional team required to achieve a safe outcome for mother and infant.
3 URLs, 1 Forum - Define abnormal labor patterns.
-
Module 2: Lesson 18: Third Trimester Bleeding
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the causes of third trimester bleeding, with an understanding of social, ethnic, and racial disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
- Describe the initial evaluation of a patient with third trimester bleeding.
- Provide a differential diagnosis for the cause of third trimester bleeding.
- List the maternal and fetal complications of placenta previa and placental abruption, and role of patient safety and quality improvement systems to optimize care.
- Describe the initial evaluation and management plan for acute blood loss, including the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
- List the indications and potential complications of blood product transfusion, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
6 URLs, 1 Forum - List the causes of third trimester bleeding, with an understanding of social, ethnic, and racial disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
-
Module 2: Lesson 19: Preterm Labor
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Identify the modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors and causes for preterm labor, including the role of social, economic, ethnic, and racial disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
- Describe the signs and symptoms of preterm labor.
- Describe the initial management of preterm labor.
- List indications and contraindications of medications used in preterm labor, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
- List the adverse outcomes associated with preterm birth, including key correlations between quality and safety principles with patient outcomes, with an understanding of economic, ethnic, and racial disparities in health outcomes for patients who experience preterm birth.
- Describe the counseling for reducing preterm birth risk, including the role of a multidisciplinary team and an understanding of social, economic, ethnic, and racial disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
4 URLs - Identify the modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors and causes for preterm labor, including the role of social, economic, ethnic, and racial disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
-
Lesson 20: Premature Rupture of Membranes
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the symptoms, signs, and diagnostic methods used to confirm rupture of membranes, with consideration of value-based care.
- Identify risk factors for premature rupture of membranes, including social and economic factors, with an understanding of ethnic and racial disparities in the care of and health outcomes for patients with premature rupture of membranes.
- Describe the risks and benefits of expectant management versus immediate delivery based on gestational age, with consideration of patient safety.
- Describe the methods to monitor maternal and fetal status during expectant management, including patient safety and quality parameters.
3 URLs - List the symptoms, signs, and diagnostic methods used to confirm rupture of membranes, with consideration of value-based care.
-
Module 2: Lesson 21: Intrapartum Fetal Surveillance
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the methods of fetal surveillance.
- Interpret intrapartum electronic fetal heart rate monitoring, including the role of an interprofessional team, with consideration of value-based care and the impact on patient safety.
2 URLs - Describe the methods of fetal surveillance.
-
Module 2: Lesson 22: Postpartum Hemorrhage
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the risk factors for postpartum hemorrhage, with an understanding of how racial and ethnic disparities impact the risks, diagnosis, care, and outcome of patients with postpartum hemorrhage.
- Construct a differential diagnosis for immediate and delayed postpartum hemorrhage.
- Develop an evaluation and management plan for postpartum hemorrhage, including consideration of available resources and the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
2 URLs, 1 Forum - List the risk factors for postpartum hemorrhage, with an understanding of how racial and ethnic disparities impact the risks, diagnosis, care, and outcome of patients with postpartum hemorrhage.
-
Module 2: Lesson 23: Postpartum Infections
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List common postpartum infections.
- List risk factors for postpartum infections.
- Describe the approach to a patient with a postpartum fever, with consideration of available resources.
- Develop an evaluation and management plan for the patient with postpartum infection, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
5 URLs, 1 Forum - List common postpartum infections.
-
Module 2: Lesson 24: Anxiety and Depression in Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Discuss the prevalence of and identify risk factors for postpartum blues, depression, and psychosis, including social, economic, ethnic, and racial factors, as well as disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
- Differentiate between postpartum blues, depression, and psychosis.
- Compare and contrast treatment options for postpartum blues, depression, and psychosis, including the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
- Recognize appropriate treatment options for mood disorders during pregnancy and lactation, including the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
4 URLs, 1 Forum - Discuss the prevalence of and identify risk factors for postpartum blues, depression, and psychosis, including social, economic, ethnic, and racial factors, as well as disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
-
Module 2: Lesson 25: Postterm Pregnancy
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Identify the normal duration of gestation.
- List the complications of prolonged gestation.
- Describe the evaluation and evidence-based management options for prolonged gestation, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
2 URLs - Identify the normal duration of gestation.
-
Module 2: Lesson 26: Fetal Growth Abnormalities
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define macrosomia and fetal growth restriction.
- Describe etiologies of abnormal growth, including effects of socio-economic status and nutrition.
- List methods of detection for fetal growth abnormalities, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe the management of fetal growth abnormalities, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety.
- List the associated morbidity and mortality of fetal growth abnormalities, with an understanding of the effect of social, economic, ethnic and racial disparities in access to care and health outcomes.
4 URLs, 1 Forum - Define macrosomia and fetal growth restriction.
-
Module 2: Lesson 27: Obstetric Procedures
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the key components of preoperative evaluation and planning, including history, physical examination, informed consent (including risks, benefits, and alternatives), surgical checklists and pre-operative time-out, including the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
- Describe common peri-operative interventions for the prevention of infection, deep venous thrombosis and other surgical complications.
- Describe key components of postoperative care, including the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
- Discuss common postoperative complications.
- Describe the communication of operative findings and complications to patient and family.
- Describe common outpatient and inpatient obstetrical procedures with their indications and possible complications, with consideration of value-based care and patient safety:
1. Ultrasound
2. Amniocentesis and chorionic villous sampling
3. Induction and augmentation of labor
4. Spontaneous vaginal delivery
5. Vaginal birth after Cesarean delivery
6. Operative vaginal delivery
7. Breech delivery and external cephalic version
8. Cesarean delivery
9. Postpartum tubal ligation
10. Cerclage
11. Newborn circumcision
5 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the key components of preoperative evaluation and planning, including history, physical examination, informed consent (including risks, benefits, and alternatives), surgical checklists and pre-operative time-out, including the role of an interprofessional team to ensure patient safety.
-
Module 2: Lesson 28: Maternal Inmunization
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand the significance of vaccinations in preventing infections in pregnant women and their potential transmission to newborns.
- Discuss infections with noteworthy fetal adverse outcomes, including:
Maternal Rubella Infection
Congenital Varicella Syndrome
Maternal Hepatitis B Infection
- Recognize vaccines contraindicated during pregnancy, specifically:
Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR)
Varicella
4 URLs - Understand the significance of vaccinations in preventing infections in pregnant women and their potential transmission to newborns.
-
Module 2: Lesson 29: Teenage Pregnancy
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand the nuances of teenage pregnancy (Adolescent sexual behavior, its spectrum and cultural implications).
- Explain the phychological and physical effect of pregnancy and parenthood on adolescents.
- Advocate for positive mental health outcomes in pregnant teenagers, recognizing the unique challenges they face.
- Describe approaches to Teen Pregnancy Prevention (CDC's Promoting Science-Based Approaches to Teen Pregnancy Prevention Using Getting to Outcomes (PSBA-GTO).
- Conduct thorough patient histories using the HEADSSS format (Home, Education, Activity, Drugs, Sex, Safety, Suicide) to gather comprehensive insights.
- Evaluate and recommend suitable options for contraception based on medical eligibility, patient preferences, and potential compliance.
6 URLs - Understand the nuances of teenage pregnancy (Adolescent sexual behavior, its spectrum and cultural implications).
-
Module 3: Gynecology
 Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
- Welcome to Module 3 of the OB/GYN content for medical students. In this module, you will learn about various topics, including contraceptive methods, pregnancy termination, vulvar and vaginal diseases, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and urinary tract infections (UTIs), pelvic floor disorders, endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, disorders of the breast, and gynecologic procedures. Throughout these lessons, you will gain knowledge about the mechanisms of action, effectiveness, and risks of contraceptive methods, as well as the impact of health policy, advocacy, and social/environmental factors on family planning and population health. You will also understand the evaluation, management, and potential complications of these conditions. This module emphasizes value-based care, patient safety, and the influence of social/environmental factors on reproductive health.
- Welcome to Module 3 of the OB/GYN content for medical students. In this module, you will learn about various topics, including contraceptive methods, pregnancy termination, vulvar and vaginal diseases, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and urinary tract infections (UTIs), pelvic floor disorders, endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, disorders of the breast, and gynecologic procedures. Throughout these lessons, you will gain knowledge about the mechanisms of action, effectiveness, and risks of contraceptive methods, as well as the impact of health policy, advocacy, and social/environmental factors on family planning and population health. You will also understand the evaluation, management, and potential complications of these conditions. This module emphasizes value-based care, patient safety, and the influence of social/environmental factors on reproductive health.
-
Module 3: Lesson 1: Family Planning
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the mechanism of action and effectiveness of contraceptive methods (Fertility Awareness-Based Methods, Barrier Methods, Hormonal Methods, Intrauterine Methods, Emergency Contraception, Sterilization).
- Identify patients eligible for a specific type of contraception method.
- Counsel the patient regarding the benefits, risks and use for each contraceptive method, including emergency contraception, and discuss how health policy, advocacy and social and environmental factors impact family planning and population health.
- Discuss barriers to effective contraceptive use and reduction of unintended pregnancy, and how health policy, advocacy, and social and environmental factors impact family planning and population health.
- Describe methods of male and female surgical sterilization.
- Explain the risks, benefits, and patient safety implications of female surgical sterilization procedures.
9 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 3: Lesson 2: Vulvar and Vaginal Disease
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Formulate a differential diagnosis for vulvovaginitis.
- Formulate a differential diagnosis for dermatologic disorders of the vulva.
- Discuss the steps in the evaluation and management of a patient with vulvovaginal symptoms, with consideration of value-based care.
- Interpret a wet mount microscopic examination.
3 URLs, 1 Forum - Formulate a differential diagnosis for vulvovaginitis.
-
Module 3: Lesson 3: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) and Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the guidelines for STI screening and partner notification/ treatment, understanding the impact on public health.
- Understand the importance of patient counseling in preventing disease spread and demonstrate effective patient counseling techniques.
- Understand how social and environmental factors can play a role in the prevalence, incidence, diagnosis, and treatment of STIs.
- Describe STI prevention strategies, including immunization, with consideration of social and environmental factors, value-based care, and population health.
- Describe the symptoms and physical exam findings associated with common STIs.
- Understand and describe the diagnostic tools and criteria for detecting STIs and UTIs.
- Discuss the steps in the evaluation and management of common STIs as part of an interprofessional team, including appropriate referral, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe the pathophysiology of salpingitis and pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Describe the evaluation, diagnostic criteria, and initial management of salpingitis/pelvic inflammatory disease, with consideration of value-based care and impact on population health and patient safety.
- Identify possible long-term sequelae of salpingitis/ pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Describe the evaluation and management of UTIs, with consideration of value-based care.
7 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the guidelines for STI screening and partner notification/ treatment, understanding the impact on public health.
-
Module 3: Lesson 4: Pelvic Floor and Abdominal Wall Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe normal adominal wall, pelvic anatomy and pelvic support.
- Understand and describe the different types of abdominal wall defects, their clinical implications, and appropriate management strategies.
- Describe signs and symptoms of pelvic floor disorders.
- List risk factors for pelvic floor disorders, including social and environmental factors that influence health outcomes for patients with pelvic floor disorders.
- Explain the pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, and diagnostic tools for Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP).
- Explain the pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, and diagnostic tools for Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injuries (OASIS) and understand its implications in postpartum care.
- Describe the clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and management strategies for urinary retention and urinary Incontinence.
- Discuss the steps in evaluation of pelvic floor disorders, with consideration of value-based care, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Describe the anatomic changes associated with pelvic floor disorders.
- Describe nonsurgical and surgical management options for pelvic floor disorders, with consideration of value-based care.
8 URLs - Describe normal adominal wall, pelvic anatomy and pelvic support.
-
Module 3: Lesson 5: Endometriosis
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe theories of pathogenesis of endometriosis.
- List the most common sites of endometriosis.
- Describe the symptoms and physical exam findings in a patient with endometriosis.
- Describe the diagnosis and management options for endometriosis, with consideration of value-based care and an understanding of any social and economic disparities in health outcomes for patients with endometriosis.
2 URLs - Describe theories of pathogenesis of endometriosis.
-
Module 3: Lesson 6: Chronic Pelvic Pain
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define chronic pelvic pain.
- Define prevalence and common etiologies of chronic pelvic pain, with an understanding of social and environmental factors.
- Describe the symptoms and physical exam findings in a patient with chronic pelvic pain.
- Discuss evaluation and management options for chronic pelvic pain, with consideration of value-based care and social and environmental factors that may lead to disparities in care and health outcomes, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Discuss the psychosocial issues associated with chronic pelvic pain and situations where advocacy and an interprofessional team approach are beneficial, with an understanding of social and environmental factors that may impact these issues.
3 URLs - Define chronic pelvic pain.
-
Module 3: Lesson 7: Disorders of the Breast
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand the anatomy and embryology of the breast.
- Describe the epidemiolgical patterns of breast diseases.
- Emphasize the importance and methods of regular breast cancer screening for early detection.
- List factors that place individuals at risk for breast disorders, with consideration of population health impact and an understanding of social and environmental factors that can lead to disparities in health outcomes for patients with breast disorders.
- Describe symptoms and physical examination findings of benign or malignant conditions of the breast.
- Demonstrate the performance of a clinical breast examination and interpreting results.
- Discuss the steps in the evaluation of common breast complaints, including mastalgia, mass, and nipple discharge, with consideration for value-based care.
- Discuss initial management options for benign and malignant conditions of the breast, with consideration of value-based care.
8 URLs - Understand the anatomy and embryology of the breast.
-
Module 3: Lesson 8: Gynecologic Procedures
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the key components of preoperative evaluation and planning, including history, physical examination and describing key elements of informed consent (including risks, benefits, alternatives and social and environmental factors that may impact informed consent).
- Discuss in-depth the ethical and legal aspects of informed consent, ensuring students can effectively communicate with patients, addressing concerns and answering questions.
-
Describe common measures for the prevention of infection, deep venous thrombosis and other perioperative complications, with key consideration for patient safety.
- Describe the components of postoperative care within a framework of interprofessional teamwork, with consideration of patient handover communication.
- Discuss common postoperative complications.
- Describe the communication of operative findings and complications to patients and family.
- Describe the key members of an operating room team within a framework of interprofessional teamwork.
- Describe key components of a preprocedural or preoperative time out.
- Understand how surgical management can emotionally impact a patient and her family, with consideration of social and environmental factors.
- Describe common outpatient and inpatient gynecologic procedures with their indications, contraindications and possible complications
1. Pelvic ultrasonography
2. Colposcopy and cervical biopsy
3. Excisional procedures of the cervix
4. Vulvar biopsy
5. Endometrial biopsy
6. IUD insertion and removal
7. Contraceptive implant placement and removal
8. Dilation and curettage
9. Hysteroscopy
10. Laparoscopy
11. Tubal ligation
12. Hysterectomy and bilateral salpingooophorectomy
13. Pregnancy termination
- Demonstrate the ability to complete procedural tasks and general procedures of a physician
1. Sterile technique
2. Foley catheter insertion
3. Basic suturing
4. Knot tying
6 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 3: Lesson 9: Congenital Anomalies of the Female Reproductive Tract
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Recall the normal anatomy of the female reproductive tract, specifically the vagina, cervix, corpus, and adnexae.
- Describe common and rare congenital anomalies of the vagina, cervix, corpus, and adnexae.
- Recognize the typical clinical presentations and associated symptoms of patients with congenital anomalies of the female reproductive tract.
- Demonstrate the ability to select and interpret appropriate imaging and diagnostic tests to evaluate suspected congenital anomalies.
- Differentiate between various congenital anomalies of the female reproductive tract and other conditions with similar presentations.
3 URLs -
Module 4: Reproductive Endocrinology, Infertility and Related Topics
 Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
- Welcome to Module 4 of the OB/GYN content for medical students! In this module, we will cover a range of topics related to reproductive health. You will learn about amenorrhea, hirsutism, abnormal uterine bleeding, dysmenorrhea, menopause, infertility, premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), as well as gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). Throughout these lessons, we will explore the pathophysiology, etiologies, evaluation, and management options for these conditions while considering value-based care, social and environmental factors, patient safety, and health disparities. By the end of this module, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these important reproductive health topics.
- Welcome to Module 4 of the OB/GYN content for medical students! In this module, we will cover a range of topics related to reproductive health. You will learn about amenorrhea, hirsutism, abnormal uterine bleeding, dysmenorrhea, menopause, infertility, premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), as well as gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). Throughout these lessons, we will explore the pathophysiology, etiologies, evaluation, and management options for these conditions while considering value-based care, social and environmental factors, patient safety, and health disparities. By the end of this module, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these important reproductive health topics.
-
Module 4: Lesson 1: Pediatric & Adolescent Gynecology
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the changes in the hypothalamicpituitary-ovarian axis and target organs during normal puberty.
- Explain the normal sequence of pubertal events and ages at which these changes occur across different patient populations.
- Discuss the psychological issues associated with puberty and how social and environmental factors may affect them.
- Define precocious and delayed puberty, and describe the steps in the initial evaluation of these conditions, with consideration of value-based care.
- Recognizing the unique needs and challenges on Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology.
- Trauma & Infections: Identify common types of gynecological trauma and infections in pediatric and adolescent patients and initiate appropriate management.
- Understand the signs, implications, and protocols associated with sexual abuse in pediatric and adolescent patients.
- Recognize the indicators of pelvic masses in pediatric and adolescent patients and understand the initial steps in evaluation and management.
- Diagnose and manage common pediatric & adolescent GYN problems, integrating knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and common pathologies.
10 URLs - Describe the changes in the hypothalamicpituitary-ovarian axis and target organs during normal puberty.
-
Module 4: Lesson 2: Normal and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the endocrinology and physiology of the normal menstrual cycle.
- Understand the Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS).
- Define abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Describe the pathophysiology and identify etiologies of abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Describe the steps in the evaluation and initial management of abnormal uterine bleeding, with an understanding of ethnic and racial disparities in health outcomes for patients who experience abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Summarize medical and surgical management options for patients with abnormal uterine bleeding, with consideration of value-based care and an understanding of the impact on patient safety.
4 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the endocrinology and physiology of the normal menstrual cycle.
-
Module 4: Lesson 3: Amenorrhea
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea.
- Explain the pathophysiology and identify the etiologies of amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea, including possible nutritional, social and environmental causes and opportunities for advocacy.
- Describe associated symptoms and physical examination findings of amenorrhea.
- Discuss the steps in the evaluation and initial management of amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea, with consideration of value-based care and the effect of social and environmental factors on care and outcomes.
- Describe the consequences of untreated amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea.
4 URLs - Define amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea.
-
Module 4: Lesson 4: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) & Androgen Excess (Hirsutism and Virilization)
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Recognize normal variations and abnormalities in secondary sexual characteristics, with an understanding of racial and ethnic differences in puberty.
- Define hirsutism and virilization.
- Describe pathophysiology and identify etiologies of hirsutism.
- Describe the steps in the evaluation and initial management options for hirsutism and virilization, with consideration for value-based care.
- Describe how hirsutism and virilization are manifested in other medical disorders.
3 URLs - Recognize normal variations and abnormalities in secondary sexual characteristics, with an understanding of racial and ethnic differences in puberty.
-
Module 4: Lesson 5: Dysmenorrhea
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define dysmenorrhea and distinguish primary from secondary dysmenorrhea.
- Describe the social and economic effects of dysmenorrhea on patients.
- Describe the pathophysiology and identify the etiologies of dysmenorrhea, including social and environmental factors.
- Discuss the steps in the evaluation and management of dysmenorrhea, with consideration of value-based care.
3 URLs - Define dysmenorrhea and distinguish primary from secondary dysmenorrhea.
-
Module 4: Lesson 6: Menopause
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define the fundamentals of menopause (Spontaneous menopause, Induced menopause, Perimenopause, Early Menopause, Premature Ovarian Insufficiency, Climacterium) Stages and types.
- Describe cultural and social expectations of women’s experience of menopause.
- Describe changes in the hypothalamicpituitary-ovarian axis associated with perimenopause/ menopause.
- Describe symptoms and physical exam findings related to perimenopause/ menopause.
- Discuss management options for patients with perimenopausal/ menopausal symptoms, with consideration of patient safety, valuebased care, and an understanding of social, environmental, and economic factors on aging.
- Counsel patients regarding the menopausal transition, effect on quality of life, and the role of social factors in promoting healthy aging.
- Counsel patients on the role of healthy lifestyle practices, including nutrition, physical activity, and substance use, in managing menopausal symptoms and healthy aging, with consideration of value-based care.
- Discuss long-term medical disorders associated with menopause, with an understanding of the gender, ethnic, and racial disparities in health outcomes
5 URLs, 1 Forum - Define the fundamentals of menopause (Spontaneous menopause, Induced menopause, Perimenopause, Early Menopause, Premature Ovarian Insufficiency, Climacterium) Stages and types.
-
Module 4: Lesson 7: Infertility
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Define infertility and distinguish between primary and secondary infertility.
- List the causes of male and female infertility.
- Describe the pathophysiology of different causes of infertility, including impact of social and environmental factors.
- Describe the evaluation and initial management of an infertile couple, with consideration of value-based care and social, economic and health systems factors that may limit access to care, as a member of an interprofessional team.
- Describe management options for infertility, with consideration of value-based care and social, economic, and health systems factors that may limit access to care.
- Identify the options for genetic screening and testing in infertility-associated treatments, with a consideration of value-based care.
- Describe ethical issues confronted by patients with infertility and patients accessing assisted reproductive technologies, including patient safety.
5 URLs, 1 Forum - Define infertility and distinguish between primary and secondary infertility.
-
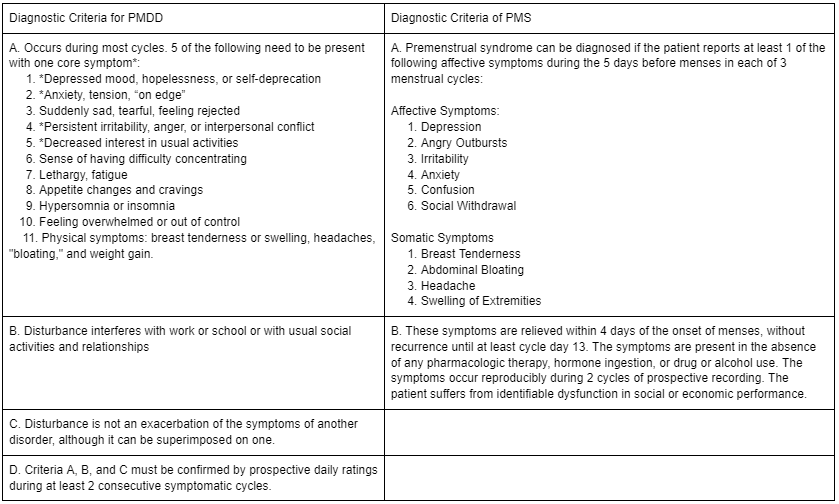
Module 4: Lesson 8: Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS), Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) and other menstrual Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Complete a history that can identify the criteria for making the diagnoses of PMS and PMDD.
- Describe treatment options for PMS and PMDD, including an interprofessional team approach, with consideration of value-based care and how they relate to patient safety and population health.
1 URL, 1 Forum - Complete a history that can identify the criteria for making the diagnoses of PMS and PMDD.
-
Module 4: Lesson 9: Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the symptoms and physical examination findings of a patient with GTN, including molar pregnancy.
- Describe the diagnostic methods, treatment options and follow-up for GTN, including molar pregnancy, with consideration of value-based care and the social and environmental factors that may influence health outcomes.
- Recognize the difference between molar pregnancy and malignant GTN, and the importance of making a correct diagnosis and initiating therapy quickly.
4 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the symptoms and physical examination findings of a patient with GTN, including molar pregnancy.
-
Module 5: Neoplasia
 Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
- Welcome to Module 5 of the OB/GYN content for medical students! In this module, we will focus on gynecologic neoplasms. You will learn about vulvar neoplasms, uterine leiomyoma, endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma, as well as ovarian neoplasms. Throughout these lessons, we will cover topics such as risk factors, symptoms, physical examination findings, diagnostic methods, management options, and the impact of social and environmental factors on health outcomes. By the end of this module, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these gynecologic neoplasms, their management, and the importance of value-based care and population health.
- Welcome to Module 5 of the OB/GYN content for medical students! In this module, we will focus on gynecologic neoplasms. You will learn about vulvar neoplasms, uterine leiomyoma, endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma, as well as ovarian neoplasms. Throughout these lessons, we will cover topics such as risk factors, symptoms, physical examination findings, diagnostic methods, management options, and the impact of social and environmental factors on health outcomes. By the end of this module, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these gynecologic neoplasms, their management, and the importance of value-based care and population health.
-
Module 5: Lesson 1: Counsel and management of Neoplasm's Patients
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Understand the psychological and emotional implications of a neoplasia diagnosis on the patient.
- Demonstrate effective communication skills to counsel patients diagnosed with neoplasms, ensuring they understand their condition, treatment options, and prognosis.
- Recognize the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing patients with neoplasms, including involving psychologists, nutritionists, and social workers.
2 URLs -
Module 5: Lesson 2: Vulvar Neoplasms
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List risk factors for vulvar neoplasms.
- Describe the symptoms and physical examination findings of a patient with vulvar neoplasm.
- List the indications for vulvar biopsy.
- List common vulvar neoplasms.
4 URLs, 1 Forum - List risk factors for vulvar neoplasms.
-
Module 5: Lesson 3: Vaginal Disease and Neoplasia
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Recognize the risk factors associated with vaginal neoplasia.
- Describe the clinical presentation and physical examination findings in a patient with vaginal neoplasia.
- Outline diagnostic modalities for vaginal neoplasia and their interpretation.
- Develop initial management plans for patients with vaginal neoplasia, understanding when conservative management is appropriate and when intervention is required.
2 URLs -
Module 5: Lesson 4: Cervical Disease and Neoplasia
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the pathogenesis of cervical cancer.
- Complete a history to identify risk factors for cervical neoplasia and cancer, with an understanding of social and environmental factors.
- List the guidelines for cervical cancer screening.
- Describe the initial management of a patient with abnormal cervical cancer screening with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe the symptoms and physical findings of a patient with cervical cancer.
- List current indications for HPV vaccination and its role in the prevention of cervical cancer.
5 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the pathogenesis of cervical cancer.
-
Module 5: Lesson 5: Uterine Leiomyoma
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Cite the prevalence of uterine leiomyoma, with consideration of population health.
- Identify symptoms and physical findings in patients with uterine leiomyoma.
- Describe diagnostic methods to confirm uterine leiomyomas, with consideration of value-based care.
- Describe the management options for treatment of uterine leiomyomas, with consideration of value-based care and the effect of social and environmental factors on health outcomes.
4 URLs, 1 Forum - Cite the prevalence of uterine leiomyoma, with consideration of population health.
-
Module 5: Lesson 6: Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia/cancer, with consideration of public health impact and social and environmental factors.
- Describe the symptoms and physical findings with endometrial hyperplasia/cancer.
- Outline the causes, diagnosis and management of postmenopausal bleeding, with consideration of value-based care and the impact of social and environmental factors on health outcomes.
3 URLs - List the risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia/cancer, with consideration of public health impact and social and environmental factors.
-
Module 5: Lesson 7: Ovarian Neoplasms
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe the initial management of a patient with an adnexal mass, with consideration of value-based care.
- Compare the characteristics of functional cysts, benign ovarian neoplasms, and ovarian cancers.
- List the risk factors and protective factors for ovarian cancer, with consideration of population health implications and the impact of social and environmental factors.
- Describe the symptoms and physical findings associated with ovarian cancer.
- Describe the three histological categories of ovarian neoplasms.
6 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the initial management of a patient with an adnexal mass, with consideration of value-based care.
-
Module 6: Human Sexuality
 Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
- Welcome to Module 6 of the OB/GYN content for medical students, where we will explore the multifaceted field of female sexual health. This module will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of female sexual dissatisfaction, its impact on physical, psychological, and social well-being, and the factors that contribute to sexual satisfaction. Through this module, you will learn to obtain a thorough sexual history, understand the physiology of the female sexual response, and identify common reasons for sexual dissatisfaction while considering the influence of social and environmental factors. We will delve into the physical, psychological, and social consequences of sexual dissatisfaction, distinguish between sexual identification and behavior, and discuss the adverse health outcomes among sexual minority individuals. Additionally, we will emphasize the role of an interprofessional team in addressing the holistic impact of sexual dissatisfaction. By the end of this module, you will be equipped to approach and manage female sexual health concerns with a patient-centered and comprehensive approach, promoting overall well-being and quality of life.
- Welcome to Module 6 of the OB/GYN content for medical students, where we will explore the multifaceted field of female sexual health. This module will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of female sexual dissatisfaction, its impact on physical, psychological, and social well-being, and the factors that contribute to sexual satisfaction. Through this module, you will learn to obtain a thorough sexual history, understand the physiology of the female sexual response, and identify common reasons for sexual dissatisfaction while considering the influence of social and environmental factors. We will delve into the physical, psychological, and social consequences of sexual dissatisfaction, distinguish between sexual identification and behavior, and discuss the adverse health outcomes among sexual minority individuals. Additionally, we will emphasize the role of an interprofessional team in addressing the holistic impact of sexual dissatisfaction. By the end of this module, you will be equipped to approach and manage female sexual health concerns with a patient-centered and comprehensive approach, promoting overall well-being and quality of life.
-
Module 6: Lesson 1: Sexuality and Modes of Sexual Expression
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Obtain a sexual history, including gender identity, sexual identity, orientation and behavior, and sexual satisfaction.
- Describe the physiology of the female sexual response.
- Describe common reasons for female sexual dissatisfaction and the contribution of social and environmental factors to sexual satisfaction.
- Describe the physical, psychological, and social impact of female sexual dissatisfaction.
- Describe the difference between sexual identification and sexual behavior, and the association of adverse health outcomes among sexual minority individuals.
- Describe the role of an interprofessional team in addressing the physical, psychological, and social impact of female sexual dissatisfaction.
7 URLs, 1 Forum - Obtain a sexual history, including gender identity, sexual identity, orientation and behavior, and sexual satisfaction.
-
Module 7: Violence Against Women
 Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
- Welcome to Module 7 of the OB/GYN content for medical students, where we will delve into the critical topics of intimate partner violence and sexual assault. This module aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and support survivors of these traumatic experiences while providing trauma-informed care. Throughout this module, you will learn about the prevalence and incidence of violence against women, elder abuse, and child abuse. You will gain the ability to screen patients for intimate partner violence and identify those at increased risk. Additionally, you will learn how to provide medical and psychological management to survivors of sexual assault while offering counseling and resources using trauma-informed care principles. By the end of this module, you will be prepared to approach and address the complex issues surrounding intimate partner violence and sexual assault while prioritizing the well-being and safety of survivors.
- Welcome to Module 7 of the OB/GYN content for medical students, where we will delve into the critical topics of intimate partner violence and sexual assault. This module aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and support survivors of these traumatic experiences while providing trauma-informed care. Throughout this module, you will learn about the prevalence and incidence of violence against women, elder abuse, and child abuse. You will gain the ability to screen patients for intimate partner violence and identify those at increased risk. Additionally, you will learn how to provide medical and psychological management to survivors of sexual assault while offering counseling and resources using trauma-informed care principles. By the end of this module, you will be prepared to approach and address the complex issues surrounding intimate partner violence and sexual assault while prioritizing the well-being and safety of survivors.
-
Module 7: Lesson 1: Sexual Assault
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Identify survivors of sexual assault, with an understanding of the principles of trauma-informed care.
- Describe the medical and psychological management of a survivor of sexual assault using principles of trauma-informed care, as part of an interprofessional team.
- Counsel survivors of sexual assault on resources available using principles of trauma-informed care.
3 URLs, 1 Forum - Identify survivors of sexual assault, with an understanding of the principles of trauma-informed care.
-
Module 7: Lesson 2: Intimate Partner Violence
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Cite prevalence and incidence of violence against women, elder abuse, and child abuse.
- Screen a patient for intimate partner violence.
- Counsel survivors of intimate partner violence on short term safety and resources available for care using principles of traumainformed care.
- Identify patients at increased risk for intimate partner violence.
6 URLs - Cite prevalence and incidence of violence against women, elder abuse, and child abuse.
-
Module 8: Osteopathy and Women’s Health Care
 Competency covered in this module:
Competency covered in this module:
- Welcome to Module 8 of the OB/GYN content for medical students, where we will explore the integration of osteopathic medicine in women's health care. This module aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to apply osteopathic principles and techniques in your practice. By the end of this module, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the basic tenets of osteopathic medicine and be able to perform a structural exam of the female patient. You will become familiar with various types of osteopathic manipulative treatments commonly used in women's health care and understand the evidence supporting their use. Additionally, you will learn how to obtain a comprehensive women's musculoskeletal history, assess lifestyle risk factors, and consider the impact of social and environmental factors on support. This module will enable you to enhance your patient care skills and promote holistic well-being in women's health.
- Welcome to Module 8 of the OB/GYN content for medical students, where we will explore the integration of osteopathic medicine in women's health care. This module aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to apply osteopathic principles and techniques in your practice. By the end of this module, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the basic tenets of osteopathic medicine and be able to perform a structural exam of the female patient. You will become familiar with various types of osteopathic manipulative treatments commonly used in women's health care and understand the evidence supporting their use. Additionally, you will learn how to obtain a comprehensive women's musculoskeletal history, assess lifestyle risk factors, and consider the impact of social and environmental factors on support. This module will enable you to enhance your patient care skills and promote holistic well-being in women's health.
-
Module 8: Lesson 1: Introduction to Osteopathic Principles in Obstetrics & Gynecology
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- List the basic tenets of osteopathic medicine.
- Perform a structural exam of the female.
- Perform the different types of osteopathic manipulative treatments (OMT) commonly used in women’s health care, including:
1. High velocity/low amplitude
2. Muscle energy
3. Myofacial release
4. Osteopathy in the cranial field
5. Strain/ counterstrain
6. Soft tissue/ articulatory techniques
7. Lymphatic treatment
8. Balanced ligamentous tension
9. Facilitated positional release
10. Progressive inhibition of neuromuscular structures
11. Functional technique
12. Visceral manipulation
13. Still technique
- Identify evidence supporting the use of OMT in ob-gyn.
3 URLs - List the basic tenets of osteopathic medicine.
-
Module 8: Lesson 2: Osteopathic History Taking
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Obtain a comprehensive women’s musculoskeletal history (e.g., scoliosis, musculoskeletal traumas, and biomechanical factors that may have influence on pregnancy and the outcome of pregnancy).
- Assess the patient for any lifestyle risk factors that may contribute to chronic somatic dysfunction.
- Obtain a thorough social history, including assessment of psychosocial support and understanding the impact of social and environmental factors on support.
3 URLs - Obtain a comprehensive women’s musculoskeletal history (e.g., scoliosis, musculoskeletal traumas, and biomechanical factors that may have influence on pregnancy and the outcome of pregnancy).
-
Module 8: Lesson 3: Osteopathic Structural Exam
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Perform an accurate osteopathic structural exam of the female patient.
- Identify areas of somatic dysfunction.
- Document all findings accurately in the patient chart, including:
1. Tenderness, asymmetry, restriction of motion, and/or tissue texture changes (TART) findings
2. Specific somatic dysfunctions
3. Spinal curves or postural influences
3 URLs - Perform an accurate osteopathic structural exam of the female patient.
-
Module 8: Lesson 4: Osteopathic Diagnosis and Management Plan
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Include somatic dysfunction as a part of the differential diagnosis when appropriate.
- Incorporate osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) approaches as indicated, with consideration of value-based care.
- Explain the indications and contraindications to osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) in pregnancy and women’s care, with an understanding of patient safety.
3 URLs - Include somatic dysfunction as a part of the differential diagnosis when appropriate.
-
Module 8: Lesson 5: Osteopathy in Obstetrics
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Describe how musculoskeletal, postural and biomechanical factors affect fertility.
- Identify patients that may benefit from treatment of somatic dysfunction before pregnancy, including patients with:
1. Short leg syndrome
2. Chronic pelvic pain
3. Chronic low back pain
- Discuss maternal musculoskeletal/ structural changes associated with pregnancy.
- Describe how osteopathic manipulation may affect the physiology of pregnancy.
- Perform musculoskeletal, postural and biomechanical screening exams throughout prenatal care, with consideration of value-based care.
- Perform the treatments for common somatic dysfunctions in pregnancy, including:
1. Round ligament syndrome
2. Pubic shear
3. Carpal tunnel syndrome
4. Low back pain
- Prepare the female pelvis for delivery via osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) in the third trimester.
- Discuss the normal and abnormal structural, musculoskeletal and biomechanical changes of the postpartum period, including:
1. Involution of the uterus and how it affects pelvic structures
2. Persistent low back pain after pregnancy
- Describe the common somatic dysfunctions of the postpartum period and describe their corresponding osteopathic manipulative treatments (OMT)
1. Symphysis diaphysis
2. Sacroilial dysfunction
3. Pubic shear
4. Low back pain
5. Breast engorgement and mastitis
6. Postpartum depression
14 URLs - Describe how musculoskeletal, postural and biomechanical factors affect fertility.
-
Module 8: Lesson 6: Osteopathy in Gynecology
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this module, students you will be able to:- Diagnose somatic dysfunction as a possible etiology for acute pelvic pain, including:
1. Iliosoas dysfunction
2. Pubic shear
a. Vertical
b. Anteriorposterior
3. Sacroiliac dysfunction
4. Sacral torsion
5. Myofascial strains
6. Restrictions of the pelvic diaphragm - Describe the musculoskeletal, structural and biomechanical factors that may be associated with chronic pelvic pain.
- List appropriate uses of osteopathic manipulative treatments (OMT) to manage both acute and chronic pelvic pain with consideration of value-based care.
- Identify possible tissue changes that are not visible by imaging for patients with a history of sexual abuse.
- Describe ways OMT can help prepare a patient for surgical gynecologic procedures.
- Discuss ways OMT can be used to decrease need for analgesics in the postoperative period, with consideration of value-based care.
- Perform OMT for the postoperative conditions, with consideration of value-based care.
8 URLs - Diagnose somatic dysfunction as a possible etiology for acute pelvic pain, including:
-
Course and Self Evaluation & Certificate

In this section, you can provide feedback about this course to help us make NextGenU.org better. Once evaluations are completed, you will be able to download your certificate of completion.
Click here give your feedback