-
GeneralGeneralTeachers
-
Management of Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care Homepage

Welcome to the Management of Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care course. This course will reinforce your foundational, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental health disorders. In addition, students will learn how to improve referral protocols and respond to psychiatric emergencies according to the Mental Health Act (MHA) while also learning about mental health promotion strategies for common mental health disorders in primary care settings. This course also gives insight into mental health disturbances related to substance use disorders, including diagnostic criteria and available treatment options. It provides students with the basic skills needed to effectively contribute to the delivery and quality of healthcare for individuals and populations worldwide regarding the management and treatment of common mental health disorders in primary care settings.
This Management of Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care course uses learning resources from accredited, world-class organizations and governmental organizations such as the American Psychiatric Association’s DSM -5, and the World Health Organization (WHO).
This course was originally developed by the FDP - School of Health Sciences. The course was redesigned by Genikka Camille Gabral, B.ED, MSc; Hugo Andres Rojas Aldieri, MD, MSc; Jean Pierre Musabyimana, MSc, MGHD; Magali Collonnaz, MD, MPH, MSc; Pablo Baldiviezo Rodriguez, MD; Reisha Narine, M.Sc., B.Sc.; Sherian Bachan, M.Sc., B.Sc; Seema Persaud, M.Sc., B.Sc.; Sara Wildman, B.Sc.; and Rhonda Prudent, B.Sc.
For publications on NextGenU.org’s courses’ efficacy, see NextGenU.org’s publication page. Subscribe to our newsletter to be notified of future updates and new courses and to be part of our community.
There are 11 modules to complete, which provide an introduction to:
- Introduction to Psychiatry: Interviews, Symptoms, Classification of Diseases, and Common Medication
- Ethical Considerations
- Mood Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders, Conduct Disorders and Eating Disorders
- Somatic Symptom Disorders
- Psychotic Disorders and Personality Disorder
- Neuropsychiatric and Neurocognitive Disorders
- Addiction-Related Disorders
- Psychiatric Disorders in Elderly and Children
- Emergencies in Psychiatric
- Mental Health Promotion
The completion time for this course is estimated at 97 hours, comprising 18 hours of learning resources, 36 hours to study content and assimilation, and 43 hours of participating in learning activities and quizzes, to assist the learners in the synthesis of learning materials. This course is equivalent to 2 credit hours.
This course requires the completion of all peer activities. At the end of each module, there is a practice quiz of 10 multiple-choice questions. After you’ve completed each lesson, quiz, and learning activity, at the end of the course, you’ll have access to a final exam consisting of 40 multiple-choice questions and a chance to evaluate this course. Participants have up to three opportunities to take the final exam and achieve the required score of >=70%. Once you’ve passed that last test, you will be able to download a certificate of completion from NextGenU.org and our course’s co-sponsoring organizations. We keep your personal information confidential, never sell any of your information, and only use anonymized data for research purposes. Also, we are happy to report your testing information and share your work with anyone (your school, employer, etc.) at your request.
Engaging with this course:
This free course is intended for primary health workers, nurses, medical students, and other health professionals who would like to learn the diagnosis, management, and treatment of mental health disorders in primary care settings.
To obtain a certificate, a learner must first register for the course and then successfully complete:
- all the reading requirements;
- all quizzes and pass with a 70% with unlimited attempts;
- all peer activities;
- all discussion forums;
- the final exam with a minimum of 70% and a maximum of 3 attempts;
- the self and course evaluation forms.
To obtain credit:
- Complete all requirements listed above for the certificate, and
- Your learning institution or workplace should approve the partner-university-sponsored NextGenU.org course for educational credit, as they would for their learner taking a course anywhere.
NextGenU.org is happy to provide your institution with:
- A link to and description of the course training so they can see all its components, including the co-sponsoring universities and other professional organization co-sponsors;
- Your grade on the final exam;
- Your work products (e.g., case study activities) and any other required or optional shared materials that you produce and authorize to share with them;
- Your evaluations -- course and self-assessments;
- A copy of your certificate of completion, with the co-sponsoring universities and other organizations listed.
To obtain a degree, NextGenU.org co-sponsors degree programs with institutional partners. To obtain a full degree co-sponsored with NextGenU.org, registrants must be enrolled in a degree program as a student of a NextGenU.org institutional partner. If you think your institution might be interested in offering a degree with NextGenU.org, contact us.
We hope you will find this a rewarding learning experience, and we count on your assessment and feedback to help us improve this training for future students.
Here are the next steps to take the course and earn a certificate.
- Complete the registration form.
- Take the pre-test.
- Begin the course with Module 1: Introduction to psychiatry: interviews, symptoms, classification of diseases, and common medication. In each lesson, read the description, complete all required readings and any required activity, as well as take the corresponding quizzes.
This course meets nationally approved standards of education developed for the addiction/substance use disorders counseling profession. This course's participants are assured that the continuing education (CE) credits provided will be accepted toward national credentialing by the NAADAC Certification Commission for Addiction Professionals (NCC AP), as well as by many of the individual state licensing/certification bodies in the addiction and other helping professions.
-
Module 1: Introduction to Psychiatry: Interviews, Symptoms, Classification of Diseases, and Common Medication
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Recognize symptoms of mental illness in conducting a psychiatric interview.
- Classify and diagnose mental disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat mental illnesses.
-
Module 1: Lesson 1: The Psychiatric Interview
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe psychiatric interviewing.
-
Describe the various phases of the psychiatric interview, including the elements of mental health examination, and additional investigative laboratory tests.
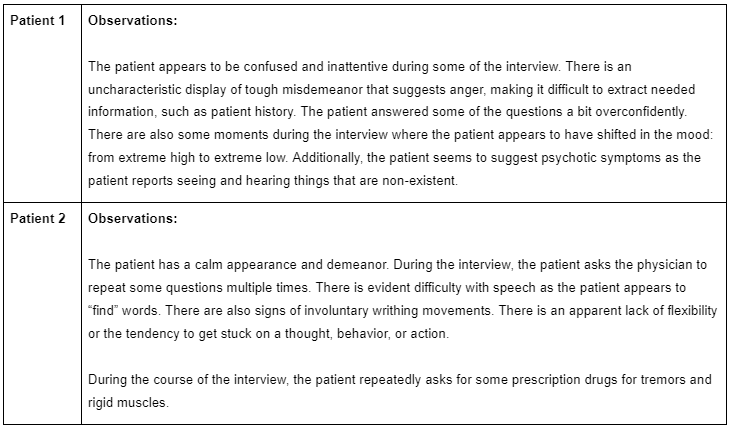
- Discuss how to apply various techniques of the psychiatric interview, including how to extract needed diagnostic information from difficult patients.
- Describe the role of empathy, active listening, and respect for privacy in the patient-physician relationship.
2 URLs - Describe psychiatric interviewing.
-
Module 1: Lesson 2: Symptoms and Signs of Psychiatric Illness
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe behavioral and emotional signs and symptoms of psychiatric illness.
-
Differentiate the levels of speech, thought, perception, and cognitive disturbances.
1 URL -
Module 1: Lesson 3: Classification in Psychiatry
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Explain DSM-V classification of classes or groups of conditions.
- Describe groups used to classify psychiatric conditions.
- Identify various rating scales to quantify aspects of a patient’s psyche, behavior, and relationships with individuals and society.
3 URLs -
Module 1: Lesson 4: Prescribing Psychiatric Medications
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Define the principles associated with prescribing psychiatric medications.
-
Discuss the risks and dangers of potentially inappropriate prescriptions to treat mental illnesses effectively.
- Describes the classification of psychiatric medications prescribed to treat common psychological and behavioral symptoms.
4 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 2: Ethical Considerations
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Understand ethical considerations relevant to treatment and management of mental health.
-
Module 2: Lesson 1: Ethics in Mental Health
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Define the principles of foundations of professional ethics.
-
Explain the principles for the protection of persons with mental illness and the improvement of mental health care.
- Describe the circumstances for emergency treatment without consent, assisted care and treatment, involuntary care, and treatment.
- Discuss the ethical implications of a breach of privacy and confidentiality in psychiatry.
3 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 3: Mood Disorders
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Classify and diagnose mood disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat mood disorders.
-
Module 3: Lesson 1: Depressive and Bipolar Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe mood disorders, bipolar disorders, and other forms of depressive illness.
- Describe major depression/other forms of depressive illness through differential diagnosis.
- Discuss the management and treatment of depressive and bipolar disorders.
4 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 4: Anxiety Disorders, Conduct Disorders and Eating Disorders
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Classify and diagnose anxiety disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat anxiety disorders.
- Classify and diagnose conduct disorders in adults and children.
- Classify and diagnose eating disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat eating disorders.
-
Module 4: Lesson 1: Anxiety Disorders, Obsessive Compulsive and Related Disorders, and Trauma-and Stressor-Related Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe anxiety disorders and its classification.
- Differentiate various types of anxiety disorders and other related disorders such as panic disorder, agoraphobia, social anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic STRESS disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and substance abuse anxiety disorder.
- Discuss the management and treatment of anxiety disorders and other related disorders.
2 URLs -
Module 4: Lesson 2: Disruptive, Impulse-control, and Conduct Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Define disruptive, impulsive-control, and conduct disorders.
-
Differentiate the categories of disruptive, impulsive-control, and conduct disorders.
2 URLs -
Module 4: Lesson 3: Feeding and Eating Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Identify the characteristics of feeding and eating disorders.
- Discuss when and how to refer patients who are diagnosed with feeding/eating disorders to a specialist.
2 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz - Identify the characteristics of feeding and eating disorders.
-
Module 5: Somatic Symptom Disorders
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Classify and diagnose somatic symptom disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat somatic symptom disorders.
-
Module 5: Lesson 1: Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe somatic symptom disorder and other related disorders in terms of their clinical features.
-
Describe the diagnostic criteria for somatic symptom disorder.
- Discuss when and how to refer patients who are diagnosed with somatic disorders to a specialist.
5 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 6: Psychotic Disorders and Personality Disorders
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Classify and diagnose psychotic disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat psychotic disorders.
- Classify and diagnose personality disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat personality disorders.
-
Module 6: Lesson 1: Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe schizophrenia as a mental health disorder and its diagnosis thereof.
- Discuss treatment and management of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders as well as admission care and treatment of assisted/ involuntary mental health users.
3 URLs -
Module 6: Lesson 2: Personality Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Identify classification of personality disorders.
- Describe clusters of personality disorders and its clinical presentation thereof.
- Discuss how personality disorders are managed and treated.
3 URLs - Identify classification of personality disorders.
-
Module 6: Lesson 3: Dissociative Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe dissociative disorders in terms of its clinical features.
-
Differentiate between various dissociative disorders.
- Discuss the management and treatment of dissociative disorders.
3 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 7: Neuropsychiatric and Neurocognitive Disorders
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Classify and diagnose neurocognitive disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat neurocognitive disorders.
- Classify and diagnose neuropsychiatric disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat neuropsychiatric disorders.
-
Module 7: Lesson 1: Neurocognitive Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Classify neurocognitive disorders (delirium and dementia).
- Describe risk factors and clinical features of neurocognitive disorders.
- Discuss how to evaluate cognitive function of a patient and how to treat neurocognitive disorders.
5 URLs - Classify neurocognitive disorders (delirium and dementia).
-
Module 7: Lesson 2: Neuropsychiatric Aspects of HIV/AIDS
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Define neuropsychiatric aspects of HIV/AIDS.
- Discuss medical treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders associated with HIV/AIDS.
- Identify drug interactions between HAART and psychiatric medication.
3 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz - Define neuropsychiatric aspects of HIV/AIDS.
-
Module 8: Addiction-related Disorders
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Classify and diagnose addiction-related disorders in adults, adolescents, and children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat addiction-related disorders.
-
Module 8: Lesson 1: Substance-related and Addictive Disorders
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe substance-related and addictive disorders and its various classes.
- Describe the different mental health disturbances related to cannabis-use and/or abuse.
- Describe diagnosis and treatment of substance-related and addictive disorders such as alcohol-use disorder, cannabis-use/abuse.
4 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 9: Psychiatric Disorders in Elderly and Children
 Competencies covered in
this module:
Competencies covered in
this module:- Classify and diagnose psychiatric disorders related to geriatric patients.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat geriatric patients with psychiatric disorders.
- Classify and diagnose psychiatric disorders in children.
- Utilize information on psychiatric drugs to effectively treat psychiatric disorders in children.
- Classify and diagnose Autism Spectrum Disorders in children.
- Recognize the needs and management principles for Autism Spectrum Disorders.
-
Module 9: Lesson 1: Geriatric Psychiatry
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Identify the most common psychiatric disorders associated with geriatric patients.
- Describe guidelines to follow when treating geriatric patients
3 URLs - Identify the most common psychiatric disorders associated with geriatric patients.
-
Module 9: Lesson 2: Depressive, Bipolar and Attention-deficit/ Hyperactive Disorders and Suicidality in Youth [Children and Adolescents]
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe depressive, bipolar, and attention deficit/hyperactive disorders, suicidality in children, its clinical features, and its risk factors.
- Describe the management and treatment of depressive, bipolar, and attention/hyperactive disorders in children.
- Design a plan to facilitate safety and support for youth diagnosed with psychiatric disorders leading to suicidality.
2 URLs -
Module 9: Lesson 3: Autism Spectrum Disorders and Adolescent and Child Psychiatry
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Identify the clinical features that will raise suspicion for ASD diagnosis and the common comorbidities associated with ASD.
- Discuss the needs and management principles of children and families with a diagnosis of ASD.
2 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 10: Emergencies in Psychiatry
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Manage psychiatric emergencies in compliance with the MHA.
- Manage psychiatric emergencies in compliance with the MHA.
-
Module 10: Lesson 1: Psychiatric Emergencies
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Define psychiatric emergencies.
-
Identify common psychiatric conditions which may constitute emergencies.
- Describe the strategies involved in the evaluation and management of patients experiencing psychiatric emergencies.
2 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 10: Lesson 2: Suicide
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe the evaluation of suicide risk.
- Describe how risk factors for suicide are assessed during a clinical examination.
- Discuss the management of suicidal patients.
2 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Module 11: Mental Health Promotion
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Introduce mental health promoting strategies.
- Introduce mental health promoting strategies.
-
Module 11: Lesson 1: Mental Health Promotion in National Policies
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe the significance of policy in mental health promotion.
- Identify examples of mental health-promoting strategies and initiatives that are already included in national health policies.
- Explain how mental health-promoting strategies can be included in national health policies.
Approximate time required to complete the readings (at 144 words/minute) and assignments for this module: 3 hours and 3 minutes.
4 URLs -
Module 11: Lesson 2: Mental Health Promotion in Different Settings
Student Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:- Describe how mental health-promoting strategies can be implemented in different settings such as homes, schools, and workplaces.
- Explain how the implementation of mental health promoting strategies in these settings create supportive environments where individuals can develop personal skills (coping skills, resilience...)
- Discuss strategies that an individual can apply on their own to promote mental health such as well-being exercises.
Approximate time required to complete the readings (at 144 words/minute) and assignments for this module: 7 hours.
5 URLs, 1 Forum, 1 Quiz -
Course and Self Evaluation & Certificate
 In this section, you can provide feedback about this course to help us make NextGenU.org better. Once evaluations are completed, you will be able to download your certificate of completion.
In this section, you can provide feedback about this course to help us make NextGenU.org better. Once evaluations are completed, you will be able to download your certificate of completion.Click here give your feedback
-
Overview
Neuropsychiatric conditions account for 13% of the total Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) lost due to all diseases and injuries in the world and are estimated to increase to 15% by the year 2020. Five of the ten leading causes of disability and premature death worldwide are psychiatric conditions.
Mental disorders represent not only an immense psychological, social and economic burden to society, but also increase the risk of physical illnesses.
It is estimated that approximately ⅓ of South Africans suffer from some form of mental disorder, according to a SASH (SA Stress and Health) study conducted in 2003/4, and ratified in 2014 by professors Dan Stein and Soraya Seedat in the Departments of Psychiatry at the University of Cape Town and the University of Stellenbosch respectively. More than 17 million people in South Africa are dealing with depression, substance abuse, anxiety, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
In recent years South Africa has taken some important steps forward in strengthening its mental health systems. Mental health legislation has been reformed and there is some level of policy commitment to mental health. However, South Africa still experiences ongoing challenges, largely related to implementation. Some of the major challenges identified include:
- The lack of officially endorsed mental health policy
- The continued low priority of mental health
- Limited intersectoral policy integration
- Stigma and discrimination
- Inadequate integration of mental with primary health care
- 'De-hospitalisation' rather than 'de-institutionalisation’
-
1. The psychiatric interview
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define psychiatric interviewing
- Identify the various phases of the psychiatric interview
- Apply the various techniques of the psychiatric interview
- Discuss how to extract the information needed for diagnosis of difficult patients
- Describe the elements of a mental status examination
- Demonstrate an understanding of investigative laboratory tests in psychiatry
-
2. Symptoms and signs of psychiatric illness
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define and describe behavioural and emotional signs and symptoms of psychiatric illness
- Describe the mental phenomena of psychiatry
- List and differentiate the levels of speech, thought, perception and cognitive disturbances
- Recognise the different psychiatric disturbances
-
3. Classification in psychiatry
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Explain DSM-V classification of classes or groups of conditions
- Define groups used to classify psychiatric conditions
- Identify various rating scales to quantify aspects of a patient’s psyche, behaviour and relationships with individuals and society
-
4. Neurocognitive disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Classify neurocognitive disorders (delirium and dementia)
- Define risk factors and clinical features of neurocognitive disorders
- Demonstrate an understanding of the treatment of neurocognitive disorders
- Demonstrate an understanding of the evaluation of cognitive function of a patient
-
5. Neuropsychiatric aspects of HIV/AIDS
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define neuropsychiatric aspects of HIV/AIDS
- Demonstrate an understanding of medical treatment of psychiatric disorders associated with HIV/AIDS
- Identify drug interactions between HAART and psychiatric medication
-
6. Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Demonstrate an understanding of schizophrenia and diagnosis thereof
- Demonstrate an understanding of other related psychotic disorders
- Discuss admission care and treatment of assisted or involuntary mental health users
- Describe the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
-
7. Depressive and bipolar disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Classify mood disorders
- Demonstrate an understanding of major depression/other forms of depressive illness
- Describe differential diagnosis of depression
- Demonstrate an understanding of the treatment of depressive and bipolar disorders
-
8. Anxiety disorders, obsessive compulsive and related disorders, and trauma-and stressor-related disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define and classify anxiety disorders
- Differentiate between panic disorder, agoraphobia, social anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Describe and differentiate between post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) and discuss the management options available to each condition
- Discuss substance-abuse anxiety disorder
- Demonstrate an understanding of the management and treatment of anxiety disorders
-
9. Personality disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience, you should be able to:
- Define and classify personality disorders
- Describe clusters of personality disorders and the clinical description thereof
- Demonstrate an understanding of the management and treatment of personality disorders
-
10. Somatic symptom and related disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define somatic symptom disorder
- Describe the diagnostic criteria for somatic symptom disorder
- Demonstrate an understanding of the clinical features of somatoform disorders
-
11. Dissociative disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Differentiate between various dissociative disorders
- Define the features of dissociate disorders
- Define the management and treatment of dissociative disorders
-
12. Disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define disruptive, impulsive-control and conduct disorders
- Categorise disruptive, impulsive-control and conduct disorders
-
13. Substance-related and addictive disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Demonstrate an understanding of substance-related and addictive disorders
- Demonstrate an understanding of the diagnosis and treatment of substance-related and addictive disorders
- Describe the different mental health disturbances related to cannabis-use and/or abuse
- Describe alcohol-use disorder and the management thereof
-
14. Feeding and eating disorders
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define the characteristics of feeding and eating disorders
- Describe the management and treatment of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa
-
15. Geriatric psychiatry
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Identify the most common psychiatric disorders associated with geriatric patients
- Describe guidelines to follow when treating geriatric patients
-
16. Depressive, bipolar and attention-deficit/ hyperactive disorders in children
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Demonstrate an understanding of depressive, bipolar and attention deficit/hyperactive disorders in children
- Describe the management and treatment of depressive, bipolar and attention/hyperactive disorders in children
-
17. Psychiatric emergencies
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define psychiatric emergencies
- Describe the strategies involved in the evaluation of patients
- Identify common psychiatric conditions which may constitute emergencies and their management
-
18. Suicide
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Describe the evaluation of suicide risk
- Define the assessment of risk factors for suicide during a clinical examination
- Demonstrate an understanding of the management and treatment of suicidal patients
-
19. Prescribing psychiatric medications
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define the principles associated with prescribing psychiatric medications
- Demonstrate an understanding of the classification of psychiatric medications
-
20. The mental health care act
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define the purpose of the mental health care act
- Identify the types of legal states to access care, treatment and rehabilitation services
- Demonstrate an understanding associated with the treatment and care of patients
- Describe the circumstances for emergency treatment without consent, assisted care and treatment, involuntary care and treatment
- Describe the role of the Mental Health Review Boards and the SA Police Service
- Define a State patient
-
21. Ethics in mental health
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Define the principles of foundations of professional ethics
- Discuss the various concepts within the Mental Health Framework
-
22. Autism spectrum disorders and adolescent and child psychiatry
Learning Outcomes
After completion of this learning experience you should be able to:
- Identify the clinical features that will raise suspicion for ASD diagnosis.
- Discuss the needs of children and families with a diagnosis of ASD.
- Manage the principles for patient and families with a diagnosis of ASD.
- Identify the clinical features that will raise suspicion of a depression diagnosis.
- Discuss the common comorbid conditions.
- Management principles for patient and families with a diagnosis of depression.
- Discuss the risk factors for suicidality.
- Design a plan to facilitate safety and support for youth with suicidality.
Management of Mental Health Disorders in Primary Care
Register for this course to access the discussion forums