-
GeneralGeneral
-
Physics Homepage

Welcome to the Physics course, part of the series for the Pre-Health Sciences Training Certificate. This course and the certificate are designed primarily for learners interested in preparing for and gaining entry to health-related programs and to help address the prerequisites for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT). This Physics course provides learners with a comprehensive overview of concepts in Physics that are necessary for developing critical thinking skills and applicable to understanding specific bodily functions. It explores the fundamental principles of Newton’s Laws, Energy, Waves, Fluids, Electricity, Light, and Magnetism.
The Physics course is sponsored in part by the International Development Research Centre and the University of the Incarnate Word School of Osteopathic Medicine. Like all NextGenU.org courses, it is competency-based, using competencies based on the Association of American Medical Colleges’ Medical College Admission Test. It uses learning resources from accredited, academic, professional, and world-class organizations and universities such as Rice University. This course was designed by Alixandria Ali BSc; Kabiru Gulma B. Pharm, MBA, MSc., Ph.D.; Marco Aurelio Hernandez, Ph.D., MSc; MSc; BSc.; Felix Emeka Anyiam, MPH, MScPH, DataSc.; Pablo Baldiviezo MD, MSc, DiplEd; Tristan Aaron Wild, BMSc (Hons); Davy Lau; and Cassandra Wild.
For publications on NextGenU.org’s courses’ efficacy, see NextGenU.org’s publication page.
There are eight (8) modules to complete, which provide an introduction to:
Module 1: Translational Motion
Module 2: Forces and Newton's Laws
Module 3: Momentum, Work, and Energy
Module 4: Waves
Module 5: Fluids and Solids
Module 6: Electricity and Magnetism
Module 7: Light and Lenses
Module 8: Atomic and Particle PhysicsThe completion time for this course is estimated at 94 hours, comprising 82 hours of learning resources and 12 hours of participating in learning activities and quizzes to assist the learners in synthesizing learning materials. This course is equivalent to 2 credit hours in the U.S. undergraduate/bachelor’s degree system.
The course requires the completion of all quizzes, discussion forums, and practical activities to receive a course certificate. Practice quizzes are available throughout the course and contain 10 Multiple-Choice Questions each. After you’ve completed each module, quiz, and learning activity, at the end of the course, you’ll have access to a final exam consisting of 40 Multiple-Choice Questions and a chance to evaluate this course. Participants have up to three opportunities to take the final exam and achieve the required passing score of >=70%. Once you’ve passed the final exam and completed the evaluations, you will be able to download a certificate of completion from NextGenU.org and our course’s co-sponsoring organizations.
We keep all of your personal information confidential, never sell any of your information, and only use anonymized data for research purposes. Also, we are happy to report your testing information and share your work with anyone (your school, employer, etc.) at your request.
Engaging with this Course:
This free course is aimed at students who have graduated from high school and want to prepare to become a health professional and/or pass the MCAT exam. You may also browse this course for free to learn for your personal enrichment. There are no requirements.
To obtain a certificate, a learner must first register for the course and then successfully complete:
- The pre-test,
- All the reading requirements,
- All quizzes and pass with 80% with unlimited attempts,
- All practical activities,
- All discussion forums,
- The final lab activity,
- The final exam with a minimum of 80% and a maximum of 3 attempts, and
- The self and course evaluation forms.
To obtain credit:- Complete all requirements listed above for the certificate, and
- Your learning institution or workplace should approve the partner-university-sponsored NextGenU.org course for educational credit, as they usually would for their learner taking a course anywhere.
NextGenU.org is happy to provide your institution with:- A link to and description of the course training so they can see all of its components, including the co-sponsoring institutions,
- Your grade on the final exam,
- Your work products (e.g., discussion forum responses) and any other required or optional shared materials that you produce and authorize to share with them,
- Your evaluations -- course and self-assessments,
- A copy of your certificate of completion with the co-sponsoring organizations listed.
To obtain a degree, NextGenU.org co-sponsors degree programs with institutional partners. To obtain a full degree co-sponsored with NextGenU.org, registrants must be enrolled in a degree program as a student of a NextGenU.org institutional partner. If you think your institution might be interested in offering a degree with NextGenU.org, contact us.We hope you will find this a rewarding learning experience, and we count on your assessment and feedback to help us improve this training for future students.
Here are the next steps to take the course and earn a certificate:
- Complete the registration form,
- Take the pre-test, and
- Begin the course with Module 1:Translational Motion. In each lesson, read the description, complete all required readings and any required activity, as well as take the corresponding quizzes.
-
Study Materials
We've utilized the Quizlet platform to create specialized flashcards designed to reinforce and test your knowledge throughout this course. Simply click the links to freely access them. Feel free to browse through our other sets of flashcards. Dive in and happy studying!
-
Module 1: Translational Motion
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Translational motion, forces, work, energy, and equilibrium in living systems.
-
Module 1: Lesson 1: Introduction
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain how the methods of science are used to make scientific discoveries.
- Compare and contrast hypothesis, theory, and law
- .Recognize commonly used SI units and the relationships between them.
- Express quantities given in SI units using metric prefixes.
2 URLs -
Module 1: Lesson 2: Vectors and Their Components
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Distinguish between scalar and vector units.
- Explain how the magnitude of a vector is defined in terms of the components of a vector.
- Identify the direction angle of a vector in a plane .
- Apply analytical methods of vector algebra to find resultant vectors and to solve vector equations for unknown vectors.
2 URLs -
Module 1: Lesson 3: Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain the relationships between instantaneous velocity, average velocity, instantaneous speed, average speed, displacement, and time.
- Calculate velocity and speed given initial position, initial time, final position, and final time.
- Represent and calculate acceleration using graphical methods .
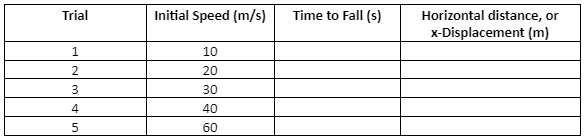
- Analyze and describe how the values of the position, velocity, and acceleration change during a free fall.
- Apply the principle of independence of motion to solve projectile motion problems.
8 URLs, 1 Forum - Explain the relationships between instantaneous velocity, average velocity, instantaneous speed, average speed, displacement, and time.
-
Module 2: Forces and Newton's Laws
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Translational motion, forces, work, energy, and equilibrium in living systems.
- Translational motion, forces, work, energy, and equilibrium in living systems.
-
Module 2: Lesson 1: Newton's Laws of Motion
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Define Newton's first law of motion, and understand the concepts of mass and inertia.
- Define Newton's second law of motion and apply the equation F(net) = ma to physics problems.
- Define Newton's third law of motion and use free-body diagrams to visualize action-reaction pairs.
- Calculate the gravitational force between two point masses.
- Distinguish between static and kinetic friction and solve physics problems involving friction.
6 URLs -
Module 2: Lesson 2: Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe Hooke’s law and simple harmonic motion, periodic motion, and oscillation.
1 URL, 1 Forum -
Module 2: Lesson 3: Uniform Circular Motion and Centripetal Force
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Solve problems involving angle of rotation and angular velocity.
- Apply Newton’s second law to develop the equation for centripetal force.
- Describe rotational kinematic variables and equations and relate them to their linear counterparts.
3 URLs -
Module 3: Momentum, Work, and Energy
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Translational motion, forces, work, energy, and equilibrium in living systems.
- Principles of chemical thermodynamics and kinetics.
- Importance of fluids for the circulation of blood, gas movement, and gas exchange.
-
Module 3: Lesson 1: Momentum, Force, and Impulse
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe momentum, impulse, and the impulse-momentum theorem.
- Describe the law of conservation of momentum.
- Distinguish between elastic and inelastic collisions.
3 URLs -
Module 3: Lesson 2: Work, Energy, and Simple Machines
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe and apply the work-energy theorem .
- Perform calculations related to kinetic and potential energy.
3 URLs -
Module 3: Lesson 3: Special Relativity
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Understand the postulates on which the special theory of relativity was based .
- Explain and perform calculations involving mass-energy equivalence .
2 URLs -
Module 3: Lesson 4: Thermal Energy, Heat, and Work
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain that temperature is a measure of internal kinetic energy .
- Solve problems involving specific heat and heat transfer .
- Solve problems involving thermal energy changes when heating and cooling substances with phase changes.
3 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 3: Lesson 5: Thermodynamics
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain the laws of thermodynamics .
- Solve problems involving thermal efficiency .
4 URLs -
Module 4: Waves
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Translational motion, forces, work, energy, and equilibrium in living systems.
- How light and sound interact with matter.
-
Module 4: Lesson 1: Types of Waves
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Distinguish a pulse wave from a periodic wave.
- Distinguish a longitudinal wave from a transverse wave .
1 URL -
Module 4: Lesson 2: Wave Properties and Interactions
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Relate wave frequency, period, wavelength, and velocity.
- Describe the interference of waves and distinguish between constructive and destructive interference of waves.
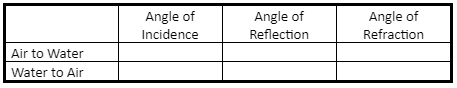
- Distinguish reflection from refraction of waves.
2 URLs -
Module 4: Lesson 3: Sound
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Relate the characteristics of waves to the properties of sound waves.
- Relate the speed of sound to the frequency and wavelength of a sound wave.
- Solve problems involving the intensity of a sound wave.
- Describe how humans produce and hear sounds.
2 URLs -
Module 4: Lesson 4: Doppler Effect, Sound Interference, and Resonance
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Calculate the frequency shift of sound from a moving object by the Doppler shift formula, and calculate the speed of an object by the Doppler shift formula.
- Contrast an open-pipe and closed-pipe resonator.
- Solve problems involving harmonic series and beat frequency.
2 URLs, 1 Forum -
Module 5: Fluids and Solids
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Importance of fluids for the circulation of blood, gas movement, and gas exchange.
-
Module 5: Lesson 1: Fluids, Density, and Surface Tension
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe the characteristics of the phases of matter at the molecular or atomic level .
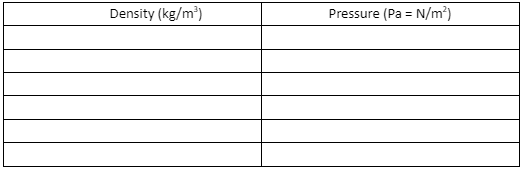
- Define density.
- Define and understand the rationale behind cohesion and adhesion.
2 URLs -
Module 5: Lesson 2: Hydrostatic Pressure and Pascal's Law
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
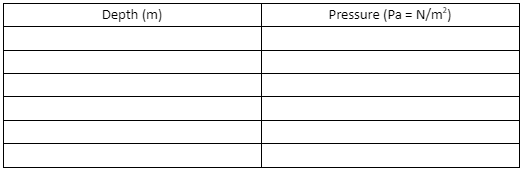
- Define density and pressure, and understand the relationship between depth in a fluid and hydrostatic pressure.
- Apply Pascal's law to a hydraulic system.
1 URL, 1 Forum -
Module 5: Lesson 3: Archimedes' Principle and Fluid Dynamics
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Understand Archimedes' principle and calculate buoyant force and specific gravity .
- Use the continuity equation to calculate the flow rate from area and velocity.
2 URLs -
Module 5: Lesson 4: Bernoulii's Equation and Venturi Effect
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Perform calculations using Bernoulli's equation.
- Apply Bernoulli's equation to a U/pitot tube.
2 URLs -
Module 5: Lesson 5: Viscosity and Turbulence and Poiseuille's Law
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Define laminar and turbulent flow, calculate viscosity, and calculate flow using Poiseuille's law.
1 URL -
Module 5: Lesson 6: Shear, Compression, Elasticity, and Plasticity
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain the concepts of stress and strain in describing elastic deformations of materials.
- Describe the range where materials show plastic behavior and the limit where the deformation of materials is elastic.
3 URLs -
Module 6: Electricity and Magnetism
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Electrochemistry and electrical circuits and their elements.
-
Module 6: Lesson 1: Charges and Coulomb's Law
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Use conservation of charge to calculate quantities of charge transferred between objects.
- Describe electric polarization and charging by induction.
- Solve problems involving Coulomb’s law.
2 URLs -
Module 6: Lesson 2: Electric Fields and Potential
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Calculate the strength of an electric field.
- Create and interpret drawings of electric fields.
- Calculate the electric potential difference between two point charges and in a uniform electric field.
- Explain the properties of capacitors and dielectrics.
3 URLs -
Module 6: Lesson 3: Electrical Circuits
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Calculate current and solve problems involving Ohm’s law.
- Calculate the equivalent resistance of resistors in a series and apply Ohm’s law to resistors in a series.
- Calculate the equivalent resistance of resistor combinations containing series and parallel resistors.
- Calculate electric power in circuits of resistors in series, parallel, and complex arrangements.
4 URLs -
Module 6: Lesson 4: Magnetic Fields, Field Lines, and Force
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe and interpret drawings of magnetic fields around permanent magnets and current-carrying wires.
- Calculate the magnitude and direction of magnetic force in a magnetic field and the force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field.
2 URLs - Describe and interpret drawings of magnetic fields around permanent magnets and current-carrying wires.
-
Module 6: Lesson 5: Motors, Generators, and Transformers
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain how electric motors, generators, and transformers work.
1 URL - Explain how electric motors, generators, and transformers work.
-
Module 6: Lesson 6: Electromagnetic Induction
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Calculate induced electromotive force and current.
1 URL, 1 Forum - Calculate induced electromotive force and current.
-
Module 7: Light and Lenses
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- How light and sound interact with matter.
-
Module 7: Lesson 1: Electromagnetic Radiation
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections.
- Solve quantitative problems involving the behavior of electromagnetic radiation.
2 URLs - Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections.
-
Module 7: Lesson 2: Lenses
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain reflection from mirrors.
- Explain refraction at media boundaries.
- Describe and predict image formation and magnification as a consequence of refraction through convex and concave lenses.
- Explain how the human eye works in terms of geometric optics.
- Perform calculations involving diffraction and interference, in particular, the wavelength of light, using data from a two-slit interference pattern.
3 URLs, 1 Forum - Explain reflection from mirrors.
-
Module 7: Lesson 3: Nature of Light
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain how photon energies vary across divisions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Describe how the photoelectric effect could not be explained by classical physics.
-
Describe the use of the photoelectric effect in biological applications, photoelectric devices, and movie soundtracks.
- Explain the particle-wave duality of light.
3 URLs - Explain how photon energies vary across divisions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
-
Module 8: Atomic and Particle Physics
 Competencies covered in this module:
Competencies covered in this module:- Atoms, nuclear decay, electronic structure, and atomic chemical behavior.
-
Module 8: Lesson 1: Radiation
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Describe the emission and absorption spectra of atoms.
-
Describe the quantum model of the atom.
- Write nuclear equations associated with the various types of radioactive decay.
- Calculate radioactive half-life and solve problems associated with radiometric dating.
- Describe how the processes of fission and fusion work in nuclear weapons and in generating nuclear power.
- Describe the ionizing effects of radiation and how they can be used for medical treatment.
5 URLs, 1 Forum - Describe the emission and absorption spectra of atoms.
-
Module 8: Lesson 2: Particle Physics
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to:Learning Objectives:
- Explain how particle accelerators work to gather evidence about particle physics.
-
Distinguish matter from antimatter.
- Define a Higgs boson and its importance to particle physics.
- Explain how grand unification theories can be tested.
3 URLs - Explain how particle accelerators work to gather evidence about particle physics.
-
Course and Self Evaluation & Certificate

In this section, you can provide feedback about this course to help us make NextGenU.org better. Once evaluations are completed, you will be able to download your certificate of completion.
Click here give your feedback