Resources Lesson 1: Developing Workforce Capacity for Public Health
A massive need for human resource development has been identified for low-income settings, in relation to the Public Health workforce requirements.
The journal Human Resources for Health is freely available online, and has a number of excellent papers - you might also like to see the paper on the Peoples-uni published in that journal.
The Global Health Workforce Alliance was established in response to this statement from its original web site: "Health workers are the heart and soul of health systems. And yet, the world is faced with a chronic shortage - an estimated 4.2 million health workers are needed to bridge the gap, with 1.5 million needed in Africa alone. The critical shortage is recognized as one of the most fundamental constraints to achieving progress on health and reaching health and development goals.
The Global Health Workforce Alliance (GHWA) was created in 2006 as a common platform for action to address the crisis. The Alliance is a partnership of national governments, civil society, international agencies, finance institutions, researchers, educators and professional associations dedicated to identifying, implementing and advocating for solutions."
The World Health Organisation has released its Global Strategy on Human Resources for Health: Workforce 2030. This is a comprehensive document with the goal to "improve health, social and economic development outcomes by ensuring universal availability, accessibility, acceptability, coverage and quality of the health workforce".
Workforce and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Two of the Sustainable Development Goals are especially relevant to our discussion on the health workforce (you can click on the button below to see more information on these two goals):
SDG 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
3.8 Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection, access to quality essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines for all
3.9c Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in least developed countries and small island developing States.
SDG 4: Ensure inclusive and equitable and quality quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
A very important paper - Forecasting imbalances in the global health labor market and devising policy responses by Scheffler et al - suggest that "To deliver essential health services required for the universal health coverage target of the Sustainable Development Goal 3, there will be a need for almost 45 million health workers in 2013 which is projected to reach almost 53 million in 2030 (across 165 countries)." The paper discuss the interaction between the health and education sectors and you can see a diagram from the paper How the labor market for health professionals relates to a country’s education and health care system. The authors continue: "The supply of health workers is a function of the training capacity in a country, net migration, deaths, and retirements." Hence there is a clear relationship between education capacity, the population and the health workforce, as expressed in SDGs 3 and 4.
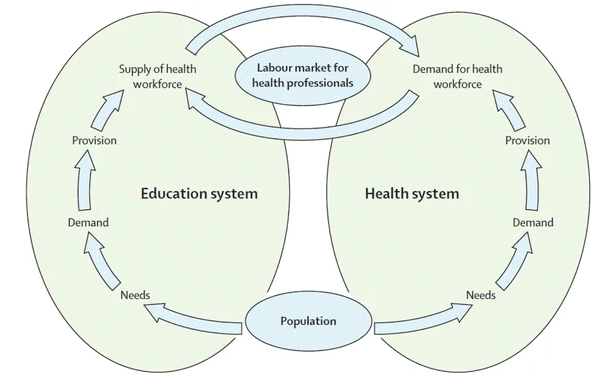
From Forecasting imbalances in the global health labor market and devising policy responses
Online global learning
Clearly addressing these challenges will require a massive effort to build workforce capacity and Peoples-uni has developed a model of online global learning: Building public health capacity through online global learning. This course, Public Health - the basics, is one of a series of Open Online Courses of designed to meet this need (see others here) . The key features of the model are:
- Online learning using Information and Communication Technology;
- Global context realising that global health challenges are relevant to all;
- Bidirectional learning between and within students and tutors in low and high income settings;
- Focus on further educational developments and delivery channels;
- Lifelong learning relevant to the stages of career progression.
The Learning Ladder below comes from the paper, and demonstrates that learning requirements evolve over the stages of career development.
